At Open Door Healthcare, we provide advanced diagnostic services like Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) and Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy (Trucut/needle biopsy). These procedures are critical tools in early diagnosis and treatment planning, offering precision, safety, and comfort to our patients.
What Are These Procedures?
Ultrasound-Guided FNAC:
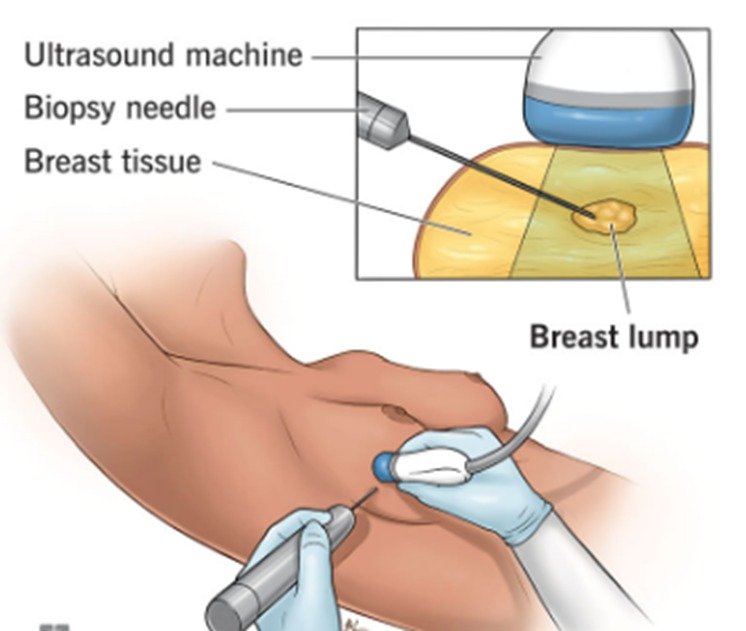
A minimally invasive procedure where a very thin needle is used to collect cells under cover of local anaesthesia from a suspicious lump or swelling under real-time ultrasound guidance. It is commonly used for evaluating lymph nodes, thyroid nodules, breast lumps, and other superficial or deep-seated abnormalities.
Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy:
This procedure involves using a needle under cover of local anaesthesia to collect a small tissue sample for detailed pathological examination known as histopathology examination and IHC (Immuno-Histochemistry) markers evaluation. It is frequently used to diagnose conditions involving the lymph nodes, breast, liver, kidneys, prostate, and other organs.
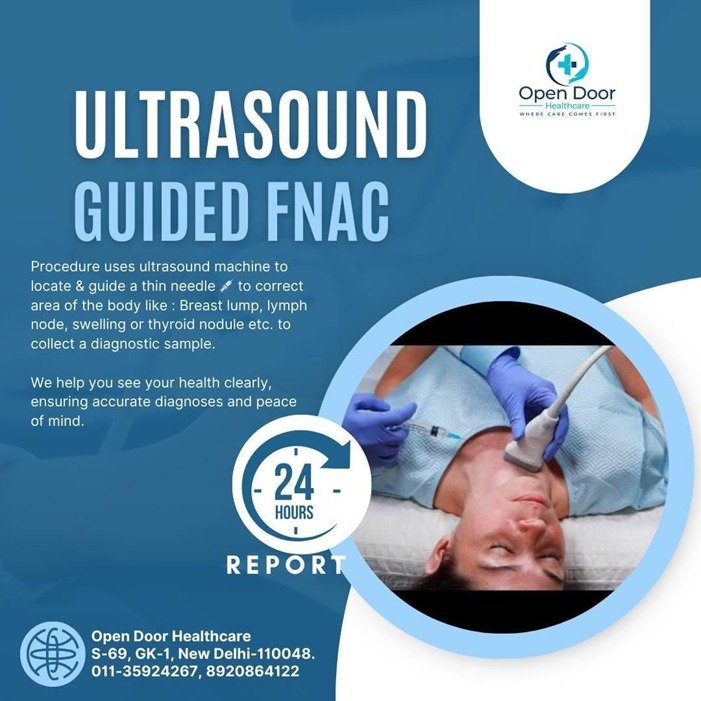
At Open Door Healthcare, our team, led by senior interventional radiologist Dr. Prashant Garg, with experience in performing over 10,000 interventional procedures. With his expertise and our state-of-the-art ultrasound equipment, we ensure accurate and efficient diagnosis.
Take the next step in your healthcare journey with confidence. Visit us at Open Door Healthcare, S-69, Greater Kailash-1, New Delhi, or call us at 011-35924267, 8920864122, 9311469699 to schedule your consultation.
Your health is in safe hands. Let us guide you to clarity and care.
FNAC stands for Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology. It is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses in the body. Using a fine, thin needle, a small sample of cells is aspirated from the suspicious area—commonly lymph nodes, thyroid, breast, or other soft tissue swellings—and then examined under a microscope.
Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) is a diagnostic test used to investigate lumps or masses in the body. It involves using a thin, hollow needle to extract a small sample of tissue or fluid from the suspected area, which is then examined under a microscope. FNAC is commonly used to assess swellings in the neck, breast, thyroid, lymph nodes, or other areas to determine whether the lump is benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). This test is minimally invasive, quick, and usually does not require anesthesia, making it a preferred initial diagnostic tool for evaluating abnormal growths or swellings.
If FNAC (Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology) is positive, it means that abnormal or malignant cells have been detected in the sample taken from the suspicious lump or swelling. This result suggests the presence of a disease, such as cancer or another pathological condition. A positive FNAC report typically prompts further diagnostic steps, including imaging tests, a biopsy, or additional laboratory evaluations, to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the disease. Based on the final diagnosis, an appropriate treatment plan—such as surgery, chemotherapy, or other medical interventions—can be developed.
A Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) biopsy is generally a quick and minimally invasive procedure that causes only mild discomfort for most patients. It involves inserting a very thin needle into the lump or mass to collect a small sample of cells for examination. While you may feel a slight pinch or stinging sensation during the needle insertion, the pain is usually brief and well-tolerated. In some cases, there may be minor soreness or bruising at the site afterward, but this typically resolves quickly. Overall, FNAC is considered a low-pain, low-risk diagnostic procedure.
A biopsy test is a medical procedure used to diagnose diseases by examining a small sample of tissue taken from the body. It helps doctors determine the presence, cause, or extent of a disease, most commonly to check for cancer or other abnormal cell growth. The tissue sample is usually collected using a needle, endoscope, or during surgery, and is then analyzed under a microscope by a pathologist. Biopsies can be performed on almost any part of the body and are essential in confirming a diagnosis, guiding treatment decisions, and monitoring disease progression or response to treatment.
A biopsy is generally not a very painful procedure, especially with the use of local anesthesia, which numbs the area where the sample is taken. Most patients describe the sensation as a quick pinch or mild discomfort rather than intense pain. The level of discomfort can vary depending on the type and location of the biopsy—for example, a skin biopsy may feel like a minor scratch, while a deeper tissue biopsy may cause some pressure or soreness afterward. Any post-procedure pain is usually manageable with over-the-counter pain relievers and subsides within a short period. If you have concerns about pain or the process, it's best to discuss them with your doctor beforehand.
Yes, a biopsy can confirm cancer. A biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small sample of tissue is removed from the body and examined under a microscope by a pathologist. It is considered the most reliable and definitive method for diagnosing cancer. By analyzing the tissue sample, doctors can determine whether cancer cells are present, what type of cancer it is, and how aggressive it may be. This information is crucial for planning the most appropriate and effective treatment for the patient.
A biopsy is not exactly like a surgery, but it is a medical procedure that may involve minor surgical techniques depending on the type and location of the tissue being sampled. In a biopsy, a small piece of tissue or cells is removed from the body to be examined under a microscope, usually to check for diseases such as cancer. Some biopsies are minimally invasive and can be done with a needle, requiring little or no anesthesia, while others might require a small incision or the use of surgical tools. Although it shares some similarities with surgery, such as the need for sterile techniques and careful handling, a biopsy is generally quicker, less invasive, and involves a shorter recovery time.

Open Door Healthcare is a multi- Specialty organization committed to providing accessible, comprehensive, and inclusive medical services to all members of the community.